Jain College Pre University II PUC Commerce Mock Question Paper 2019 : Sri Bhagawan Mahaveer Jain College
Name of the Organization : Sri Bhagawan Mahaveer Jain College
Name Of The Exam : Mock Question Paper
Document Type : Model Question Paper
Subject : Commerce
Course: II PUC – Pre University
Year : 2019
Website : https://www.jaincollege.ac.in/
Jain College II PUC Commerce Mock Model Paper
Jain College, Jayanagar
MOCK PAPER – I, Jan – 2019
Subject: II PUC Business Studies (27)
Duration: 3 hours 15 minutes
Max. Marks: 100
Related : Sri Bhagawan Mahaveer Jain College Pre University II PUC Languages Mock Question Paper 2019 : www.pdfquestion.in/33315.html
Business Studies
SECTION A :
I. Answer any TEN of the following questions. Each carries one mark: (1×10=10)
1. Give an Example for middle level Management?
2. Who is called as the father of scientific management?
3. What is the first step in planning process?
4. What is Decentralision?
5. Which one the following is not a function of staffing.
a) Recruitment B) Training C) Compensation D) Directing.
6. What is Motive?
7. What is standard in controlling process?
8. Give an Example for Fixed Assest.
9. Expand SEBI.
10. Give the meaning of product.
11. In which year consumer protection Act was enacted?
12. State any one characteristic of entrepreneurship.
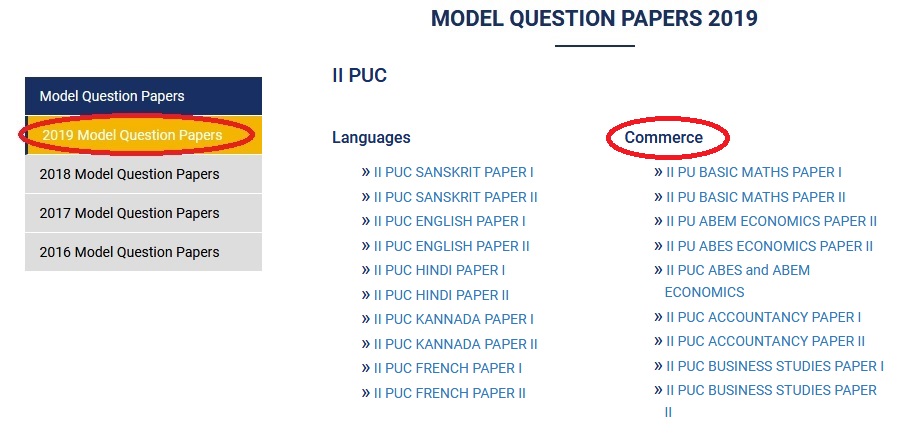
Download Question Paper :
Maths :
https://www.pdfquestion.in/uploads/pdf2019/33354-IIMat1.pdf
Abes Economics :
https://www.pdfquestion.in/uploads/pdf2019/33354-IIECO1.pdf
Abes & Abem Economics :
https://www.pdfquestion.in/uploads/pdf2019/33354-IIABEM2.pdf
Accountancy :
https://www.pdfquestion.in/uploads/pdf2019/33354-IIACC1.pdf
Business Studies :
https://www.pdfquestion.in/uploads/pdf2019/33354-IIBS1.pdf
Statistics :
https://www.pdfquestion.in/uploads/pdf2019/33354-IISTAT1.pdf
SECTION B :
II. Answer any TEN of the following questions. Each carries TWO marks: (2×10=20)
13. State any two Organizational objectives of management.
14. Define Principles of management.
15. What is the meaning of Business Environment?
16. What is a Policy? Give an Example.
17. Give the Meaning of formal organization.
18. What is Communication?
19. State any two traditional Techniques of managerial control
20. State any two objectives of financial planning.
21. Give any two Examples for durable products.
22. Who can file a complaint before the appropriate consumer forum
23. What is Entrepreneurship?
24. State any two competencies for Entrepreneurship as identified by EDI.
Accountancy
Section – A :
I. Answer any EIGHT of the followingquestions each carrying one mark: 8 × 1 = 8
1. What is motive of Not for profit organisation?
2. State any one feature of partnership.
3. _________ accounts is debited for the increase in the value of an asset.
4. In the absence of any information regarding the acquisition of share in the profit of the retiring / deceased partner by the remaining partners, it is assumed that they will acquire his / her share:-
a) Old Profit Sharing Ratio b) New Profit Sharing Ratio c) Equal Ratio d) None of the above
5. Forfeiture of share is cancellation of the rights of shareholders:-True or False.
6. Premium on issue of debenture is a ________
7. Give an example of ‘other income’.
8. Comparative statement are also known as:-
a) Dynamic Analysis b) Horizontal Analysis c) Vertical Analysis d) External Analysis
9. Expand EPS
10. What is cash flow statement?
Section – B :
II. Answer any FIVE of the following questions each carrying two marks: 5 × 2 = 10
11. What is ‘subscription’ in case of not-profit organisation?
12. State any two features of partnership?
13. Goodwill of the firm is valued at two years purchase of the average profit of last four years the total profits for last four years is Rs.40,000. Calculate goodwill of the firm.
14. Give the journal entry for sale of assets on dissolution of a firm.
15. What do you mean by over subscriptions?
16. Give the meaning of financial statements?
17. Give the formula for percentage change in comparative statements
18. Give two examples for cash outflows from operating activities?
Section – C :
III. Answer any FOURquestions, each carrying six marks: 4 × 6 = 24
19. X and Y are partners commenced Partnership business on 1.1.2016 sharing profits and losses in 3:2 ratio with capitals of Rs.1,00,000 and 80,000 respectively. They earned profits of Rs.25,000 for the year before allowing:
a) Interest on capitals @10% p.a.
b) Interest on drawing: X Rs.1,000 and Y Rs.800
c) Commission payable to X Rs.2,000
d) Salary payable to Y Rs.3,000 Prepare P and L Appropriate A/c for the year ending 31.12.2016.
20. Ankit, Suchit and Chandru are partners is a firm sharing profits and Losses in the ratio of 4:3:2. Ankit retires from the firm. Suchit and Chandru agreed to share in the ratio of 5:3 in Future. Calculate gain ratio of Suchit and Chandru.
ABES Economics
Part A :
I. Choose the correct answer: 1*5=5
1. Ordinal Utility analysis expresses utility in
a) Numbers b) Returns
c) Ranks d) Awards
2. The rate at which RBI lends money to commercial banks against securities
a) Bank rate b) Repo rate
c) Reverse repo rate d) None of the above
3. Consumption which is independent of income is called
a) Induced consumption b) autonomous consumption
c) Wasteful consumption d) past consumption
4. The study of national income related to
a) Micro economics b) Macro economics
c) Both micro and macro c) None of the above
5. The consumer and producers can choose between domestic and foreign goods, this market linkage is called
a) Financial market linkage b) Output market linkage
c) Labour market linkage d) none of the above
II. Fill in the blanks: 1*5=5
6. In the long run, all inputs are__________
7. For a price taking firm marginal revenue is equal to__________.
8. If the supply curve shifts rightwards and demand curve shifts leftwards equilibrium price will be _____________.
9. Economic exchanges without the use of money are referred to as____________
10. The Bretton Woods conference held in the year____________.
III. Match the Following: 1*5=5
11. A B
1. SDR a) Operation of invisible hand
2. Raw material b) Paper gold
3. Circulation of coin c) Trade in goods and service
4. Adam Smith d) Government of Indi
5. BOP e) intermediate good
IV. Answer in one sentence each: 1*5=5
12. What is utility?
13. How do we get personal disposable income?
14. What is balance of payment?
15. Give the meaning of supernormal profit.
16. What is price floor?
Part B :
V. Answer any NINE of the following in about four sentences each: 2*9=18
17. Distinguish between micro and macro economics.
18. Mention two approaches which explain consumer behavior.
19. What are long run costs?
20. Give the meaning of price elasticity of supply and write its formula.
21. Define equilibrium price and quantity.
22. State the relationship between marginal revenue and price elasticity of demand.
23. What do you mean by externalities? Mention its types.
24. Distinguish between stock and flow. Give example.
25. Mention the motives of demand for money.
26. What are the factors which cause change in aggregate demand?
27. Distinguish between surplus budget and deficit budget.
28. Give the meaning of managed floating exchange rate.
29. What is balance of trade?
ABEM & ABES Economics
Part A :
I. Choose the correct answer: 1×5=5
1. Which of the following is an example of micro study?
a) National income
b) Consumer behaviour
c) Unemployment
d) foreign trade
2. Ordinal utility analysis expresses utility in
a) Numbers
b) Returns
c) Ranks
d) Awards
3. The year of Great depression
a) 1920
b) 1889
c) 1929
d) 2018
4. By deducting undistributed profit from national income, we get
a) Personal Disposable income
b) Personal income
c) Private income
c) Subsidies
5. The important tool by which RBI influences money supply is
a) Open market operation
b) Closed market operation
c) Money operation
d) None of the above
II. Fill in the blanks: 1×5=5
6. In a centrally planned economy all important decisions are made by__________.
7. As income increases, the demand curve for normal goods shifts towards__________.
8. Macro economics tries to address situation facing the economy _____________.
9. __________ are defined at a particular point of time.
10. The principal motive for holding money is to carry out___________
III. Match the Following: 1×5=5
11. A B
1. Positive economics a) Functioning of mechanism
2. M3 and M4 b) Broad money
3. Excess demand c) leads to rise in the prices in the long run
4. Possibility of supernormal profit d) Zero profit
5. Normal profit e) Attraction of new firms
IV. Answer in one sentence each: 1×5=5
12. What is utility?
13. What is demand?
14. Name the well known work of Adam smith?
15. What is time deposit?
16. What is equilibrium price?
Part B :
V. Answer any NINE of the following in about four sentences each: 2×9=18
17. What is the difference between budget line and budget set?
18. Who are macro economic decision makers?
19. What do you mean by final goods?
20. Write any two possible ways in which simultaneous shift of both demand and supply curves.
21. Write the difference between Public provision and Public production.
22. Mention the non-tax revenues of the central Government.
23. Give the meaning of MRS.
24. Distinguish between micro and macro economics.
25. State the law of demand.
26. Give the meaning of the concepts of short run and long run.
27. Give the meaning of price elasticity of supply and write its formula.
28. Distinguish between stock and flow. Give example.
29. Mention any two functions of money.